Spectroscopy
Shaun Williams, PhD
What is Spectroscopy
- Spectroscopy is the area of science concerned with the absorption, emission, and scattering of electromagnetic (EM) radiation by atoms and molecules.
- Visible EM radiation is called light
- Spectroscopy played a key role in the development of quantum mechanics
- A spectrum is a graph that shows the intensity of radiation at different wavelengths
- This is also the response of atomic or molecular systems to different wavelengths of radiation
Example of Spectra
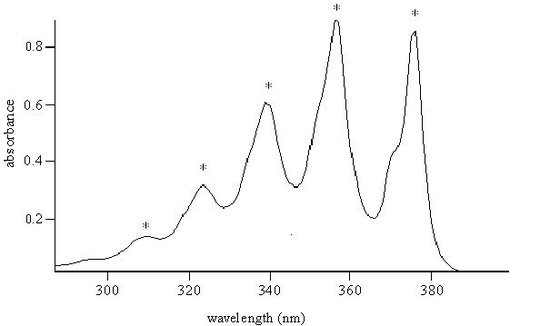
The UV Spectrum of Antracene
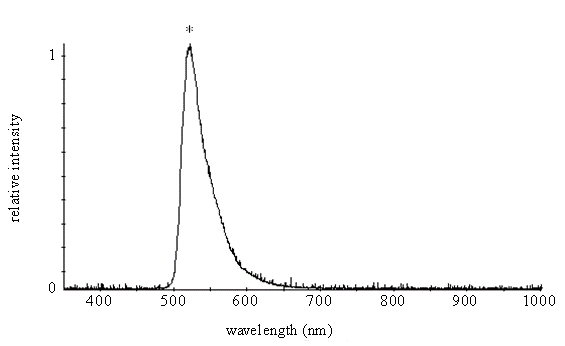
The Fluorescence Spectrum of Fluorescein
Absorption Spectra
- Absorption spectra show how much light is absorbed by a sample at each wavelength
- Absorption spectra generally are displayed with a y-axis of either:
- Transmission (\(T\))
- Absorbance (\(A\))
- Absorption Coefficient (\(\varepsilon\))
- The absorbance is called the optical density (\(OD\))
- We define \(I_0\) as the intensity of light incident on a sample
- \(I\) is the intensity of the light transmitted by the sample
- \(d\) is the thickness of the sample and \(c\) is the concentration of the absorbing species
Transmission, Absorbance, and Absorption Coefficient
$$ \begin{align} T &= \frac{I}{I_0} \\ A &= \log_{10} \frac{I_0}{I} \\ \varepsilon &= \frac{1}{dc} \log_{10} \left( \frac{I_0}{I} \right) \end{align} $$
Why so many different ways?
- Each method of plotting has particular advantages
- The transmission function is simple
- The absorbance condenses large variations by using a logarithm
- The absorbance is proportional to a fundamental property, the absorption coefficient
- The absorption coefficient can be calculated from the transition moment, which is a quantum mechanical quantity
Energy Release
- Energy is often released from atoms, molecules, and solids as light
- This light is luminescence in general
- This light is called fluorescence and phosphorescence in particular situations identified by the decay time of the luminescence and the nature of the excited state
- The decay time is the characteristic time it takes for the luminescence to disappear after the source of energy is removed or turned off
- Fluorescence decays quickly (\(\mu s\) or faster)
- Phosphorescence decays slowly (\(ms\) to minutes)
Light Scattering
- In scattering, light incident on an atomic or molecular system is deflected to some other direction
- In the scattering process, the wavelength of the light may or may not change
- If the wavelength does not change it is called elastic or Rayleigh scattering
- If the wavelength does change it is called inelastic or Raman scattering
- Rather than plotting the absolute wavelength on the x-axis, it is common to plot the change in the wavenumber value for the radiation, because this quantity is proportional to the energy left behind in the molecule during the scattering process
Spectra Characteristics
- Spectra are characterized by intense features called spectra bands or line
- Spectral bands are characterized by three quantities
- their location on the x-axis
- their intensity or height
- their width or shape
- Quantum mechanics is needed to understand and explain these characteristics
- In this course we learn how to calculate the positions of bands on the x-axis in terms of energy levels and the intensities in terms of transition moments
- The band widths and shapes are due to dynamical effects that are beyond the scope of this course
Electromagnetic Radiation
- Maxwell provided a theory that electromagnetic radiation consists of two sinusoidally oscillating fields or waves, an electric field and a magnetic field
- In the simplest situation (radiation in a vacuum), these fields oscillate perpendicularly to each other and perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave
- There are various units for electromagnetic radiation: hertz (\(Hz\)), joules (\(J\)), electron volts (\(eV\)), wavenumbers (\(cm^{-1}\)), Angstroms (\(\AA\)), and nanometers (\(nm\))
- Since wavenumbers and frequency are proportional to energy, spectroscopists often measure energy in these units for convenience
Regions of the EM Spectrum
- The electromagnetic spectrum commonly is split into regions
- These regions are classified by the nature of the instrumentation
- The different radiation frequencies correspond to different kinds of motions or degrees of freedom with a molecule
- rotational motion - microwave region
- vibrational motion - infrared region
- electronic motion - generally visible through soft x-ray regions
- nuclear and electron spin motion - radio and microwave regions
Parameters of EM Radiation
| Parameter Name | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Energy | \(E\) |
| Frequency | \(\nu\) (or \(f\)) |
| Wavelength | \(\lambda\) |
| Wavenumbers | \(\widetilde{\nu}\) |
| Speed of light in a vacuum | \(c=2.99792458\times 10^8\frac{m}{s}\) |
| Planck's Constant | \(h=6.62607004\times 10^{-34} J\cdot s\) |
Relationships Between EM Radiation Parameters
The following are useful mathematical relationships between the various EM radiation parameters $$ \begin{align} E &= \frac{hc}{\lambda} \\ E &= hc\widetilde{\nu} \\ E &= h\nu \end{align} $$
/