Introduction to Molecular Symmetry
Shaun Williams, PhD
Introduction
- Symmetry is important in chemistry
- A molecule is symmetrical if it stays indistinguishable after some movement
- The study of symmetry has many applications
- The mathematical representation of symmetry is called group theory
Symmetry Operations and Elements
- Symmetry operation is a process, like rotation, at the end of which we compare the result to the original molecule to see if they are identical
- A symmetry element refers to the axis of rotation or the mirror plane containing the molecule.
- There are five types of operational elements for symmetry
Types of Elements and Operations
| Element |
Operation |
Symbol |
| Identity |
identity |
\(E\) |
| Symmetry plane |
reflection in the plane |
\(\sigma\) |
| Inversion center |
inversion of a point \(x,y,z\) to \(-x,-y,-z\) |
\(i\) |
| Proper axis |
rotation by \(\left(\bfrac{360}{n}\right)^\circ\) |
\(C_n\) |
| Improper axis |
rotation by \(\left(\bfrac{360}{n}\right)^\circ\), followed by reflection in plane perpendicular to the rotation axis |
\(S_n\) |
Identity (\(E\))
- All molecules have this element
Symmetry Plane (\(\sigma\))
Mirror planes of the molecules:
- \(\sigma_h\) (horizontal): horizontal plane perpendicular to principle axis
- \(\sigma_d\) (dihedral): \(\sigma\) parallel to \(C_n\) and bisecting two \(C_2'\) axes
- \(\sigma_v\) (vertical): vertical plane parallel to principle axis
Inversion (\(i\))
- Inversion is a center of symmetry of a molecule
- It is a point at the center of the molecule that can transform \((x,y,z)\) into \((-x,-y,-z)\) coordinate
Proper Rotation (\(C_n\))
- Rotation with respect to an axis of rotation (the highest axis of rotation)
Improper Rotation (\(S_n\))
- It is a combination of a rotation with respect to an axis of rotation (\(C_n\)), followed by a reflection through a plane perpendicular to the \(C_n\) axis (\(\sigma_h\))
- In short, \(C_n\) followed by \(\sigma_h\)
\[ \sigma \cdot C_n = S_n \]
Successive Operations
- Sometimes, new symmetry operations form by performing two or more simpler successive operations
- We already so an example of this, improper rotation, \(S_n=C_n\times \sigma_h\)
- Another example is the inversion center, \(i=C_2 \times \sigma_h\)
- Note that \(i=S_2\)
- Any symmetry operation can be carried out multiple times in a row and in some case it can regenerate the original such as \(C_n^n=E\)
Point Groups
- Points groups are used to describe molecular symmetries
- They are a condensed representation of the symmetry elements that a molecule may possess.
- This includes both bond and orbital symmetry
- They also give rise to a character table which is a complete set of irreducible representations for a point group
- I have included a flowchart to aid in determine the point group of molecules in this module.
Point Group Components
- Point groups usually consist (but are not limited to) the following elements
- \(E\) - the identity operator
- \(C_n\) - The proper axis of rotation (the proper rotation with the highest value of \(n\) is known as the major axis of rotation
- \(\sigma\) - The mirror plane
- \(i\) - The inversion center
Non Axial Groups
- Have very little symmetry
- \(C_1\) - Elements: \(E\)
- \(C_i\) - Elements: \(E\), \(i\)
\(C_n\) Groups
- \(C_2\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_2\)
- \(C_3\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_3\), \(C_3^2\)
\(D_n\) Groups
- \(D_2\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_2(z)\), \(C_2(y)\), \(C_2(x)\)
- \(D_3\) - Elements: \(E\), \(2C_3\), \(3C_2\)
\(C_{nv}\) Groups
- \(C_{2v}\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_2\), \(\sigma_v(xz)\), \(\sigma_v'(yz)\)
- \(C_{3v}\) - Elements: \(E\), \(2C_3\), \(3\sigma_v\)
\(C_{nh}\) Groups
- \(C_{2h}\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_2\), \(i\), \(\sigma_h\)
- \(C_{3h}\) - Elements: \(E\), \(C_3\), \(C_3^2\), \(\sigma_h\), \(S_3\), \(S_3^3\)
\(D_{nh}\) Groups
- \(D_{2h}\) - Elements: \(E\), \(3C_2(z)\), \(i\), \(3\sigma\)
Character Tables - An Introduction
- A character table contains all the symmetry information of molecules in that point group
- This information can be used to analyze the molecule's behavior in many applications
Analysis of An Character Table
| \(C_{2v}\) |
\(E\) |
\(C_2(z)\) |
\(\sigma_v(xz)\) |
\(\sigma_v(yz)\) |
\(h=4\) |
|
| \(A_1\) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
\(z\) |
\(x^2,y^2,z^2\) |
| \(A_2\) |
1 |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
\(R_z\) |
\(xy\) |
| \(B_1\) |
1 |
-1 |
1 |
-1 |
\(x,R_y\) |
\(xz\) |
| \(B_2\) |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
1 |
\(y,R_x\) |
\(yz\) |
- The first column is called the Mulliken Symbol
The First Column - Mulliken Symbol
- \(A\) - (singly degenerate or one dimensional) symmetric with respect to rotation of the principle axis
- \(B\) - (singly degenerate or one dimensional) anti-symmetric with respect to rotation of the principle axis
- \(E\) - (doubly degenerate or two dimensional)
- \(T\) - (triply degenerate or three dimensional)
- Subscript \(1\) - symmetry with respect to the \(C_n\) principle axis, if no perpendicular axis then it is with respect to \(\sigma_v\)
- Subscript \(2\) - anti-symmetry with respect to the \(C_n\) principle axis, if no perpendicular axis then it is with respect to \(\sigma_v\)
- Subscript \(g\) - symmetric with respect to the inverse
- Subscript \(u\) - anti-symmetric with respect to the inverse
- prime - symmetric with respect to \(\sigma_h\)
- double prime - anti-symmetric with respect to \(\sigma_h\)
The First Row of the Character Tables
- \(E\) - describes the degeneracy of the row (\(A\) and \(B=1\)) (\(E=2\)), (\(T=3\))
- \(C_n\) - \(\bfrac{2\pi}{n}=\) number of turns in one circle on the main axis without changing the look of the molecule
- \(C_n'\) - \(\bfrac{2\pi}{n}=\) number of turns in one circle perpendicular to the main axis without changing the look of the molecule
- \(C_n''\) - \(\bfrac{2\pi}{n}=\) number of turns in one circle perpendicular to the \(C_n'\) and the main axis without changing the look of the molecule
- \(\sigma'\) - reflection of the molecule perpendicular to the other \(\sigma\)
The First Row of the Character Tables - Continued
- \(\sigma_v\)(vertical) - reflection of the molecule vertically compared to the horizontal highest fold axis
- \(\sigma_h\) or \(\sigma_d\) (horizontal) - reflection of the molecule horizontally compared to the horizontal highest fold axis
- \(i\) - inversion of the molecule from the center
- \(S_n\) - rotation of \(\bfrac{2\pi}{n}\) and then reflected in a plane perpendicular to rotation axis
- \(\#C_n\) - the # stands for the number of irreducible representation for the \(C_n\)
- \(\#\sigma\) - the # stands for the number of irreducible representations for the \(\sigma\)s
- the number in superscript - in the same rotation there is another rotation
Other Useful Definitions
- \((R_x,R_y)\) - the (,) means they are the same and can be counted once
- \(x^2+y^2,z^2\) - without (,) means they are different and can be counted twice.
| \(C_{2v}\) |
\(E\) |
\(C_2(z)\) |
\(\sigma_v(xz)\) |
\(\sigma_v(yz)\) |
\(h=4\) |
|
| \(A_1\) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
\(z\) |
\(x^2,y^2,z^2\) |
| \(A_2\) |
1 |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
\(R_z\) |
\(xy\) |
| \(B_1\) |
1 |
-1 |
1 |
-1 |
\(x,R_y\) |
\(xz\) |
| \(B_2\) |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
1 |
\(y,R_x\) |
\(yz\) |
Vibrational Spectroscopy
- The different possible vibrations are called vibrational modes
- The number of vibrational degrees of freedom differs from the total number of degrees of freedom by subtracting translations and rotations
- Linear Molecules: \(\text{number vibrational modes}=3N-5\)
- Nonlinear Molecules: \(\text{number vibrational modes}=3N-6\)
- Vibrational Modes are active in the infrared if they result in a change in the dipole moment of the molecule
- Vibrational Modes are Raman active they result in a change in the polarizability of the molecule
Determining IR Active Modes - and Raman
- Draw the molecule and draw the vibrational motion as arrows
- Determine what character that vibration transforms as
- The dipole moment transforms as \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\) in the second to last column of the character table
- Any vibrations modes in the same character as one of dipole moments will be IR active
- The polarizability transforms as the last column in the character table (eg. \(x^2\), \(9x^2-y^2\))
Examples
- Water, \(H_2O\)
- Methane, \(CH_4\)
Water
| \(C_{2v}\) |
\(E\) |
\(C_2(z)\) |
\(\sigma_v(xz)\) |
\(\sigma_v(yz)\) |
\(h=4\) |
|
| \(A_1\) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
\(z\) |
\(x^2,y^2,z^2\) |
| \(A_2\) |
1 |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
\(R_z\) |
\(xy\) |
| \(B_1\) |
1 |
-1 |
1 |
-1 |
\(x,R_y\) |
\(xz\) |
| \(B_2\) |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
1 |
\(y,R_x\) |
\(yz\) |
Methane
| \(T_d\) |
\(E\) |
\(8C_3\) |
\(3C_2\) |
\(6\sigma_d\) |
\(6S_4\) |
|
|
| \(A_1\) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
\(x^2+y^2+z^2=r^2\) |
| \(A_2\) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
|
|
| \(E\) |
2 |
-1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
\((x^2-y^2,3z^2-r^2)\) |
| \(T_1\) |
3 |
0 |
-1 |
-1 |
1 |
\((R_x,R_y,R_z)\) |
|
| \(T_2\) |
3 |
0 |
-1 |
1 |
-1 |
\((x,y,z)\) |
\((xy,yz,zx)\) |
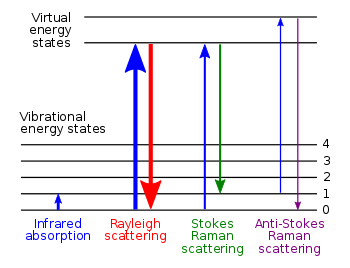
What is Raman Spectroscopy
- If a photon has energy that is significantly higher than the energy of the vibrational states, it may either be
- deflected without any change - called Rayleigh scattering
- absorbed and re-emitted at a lower energy (energy was absorbed) - called Stokes scattering
- absorbed and re-emitted at a higher energy (energy was lost) - called anti-Stokes scattering
/




