Chapter 2
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
Shaun Williams, PhD
The Early History of Chemistry
Early History of Chemistry
- Greeks were the first to attempt to explain why chemical changes occur.
- Alchemy dominated for 2000 years.
- Several elements discovered.
- Mineral acids prepared.
- Robert Boyle was the first "chemist".
- Performed quantitative experiments.
- Developed first experimental definition of an element.
Fundamental Chemical Laws
Three Important Laws
- Law of conservation of mass (Lavoisier):
- Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Law of definite proportion (Proust):
- A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass.
- Law of multiple proportions (Dalton):
- When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's Atomic Theory (1808)
- Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms.
- The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in some fundamental way or ways.
- Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms.
- Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms - changes in the way they are bound together.
- The atoms themselves are not changed in a chemical reaction.
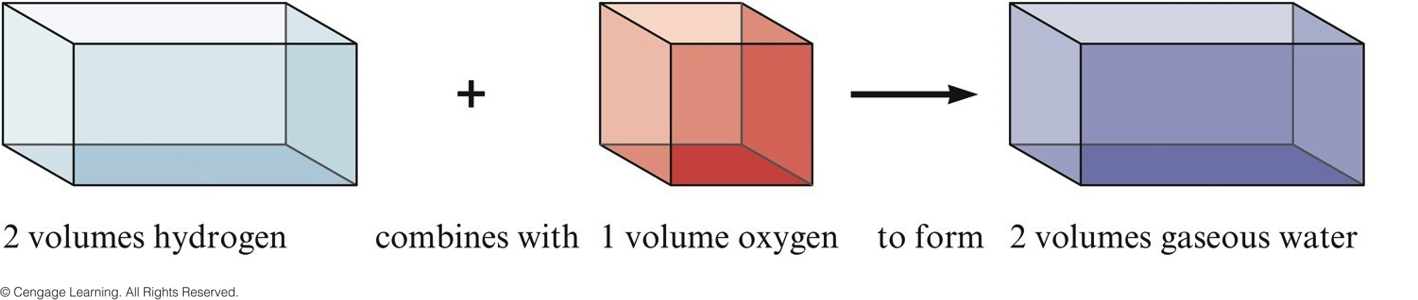
Gay-Lussac and Avogadro (1809-1811)
- Gay—Lussac
- Measured (under same conditions of T and P) the volumes of gases that reacted with each other.
- Avogadro’s Hypothesis
- At the same T and P, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of particles.
- Volume of a gas is determined by the number, not the size, of molecules.
- At the same T and P, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of particles.
representing Gay-Lussac's Results 1
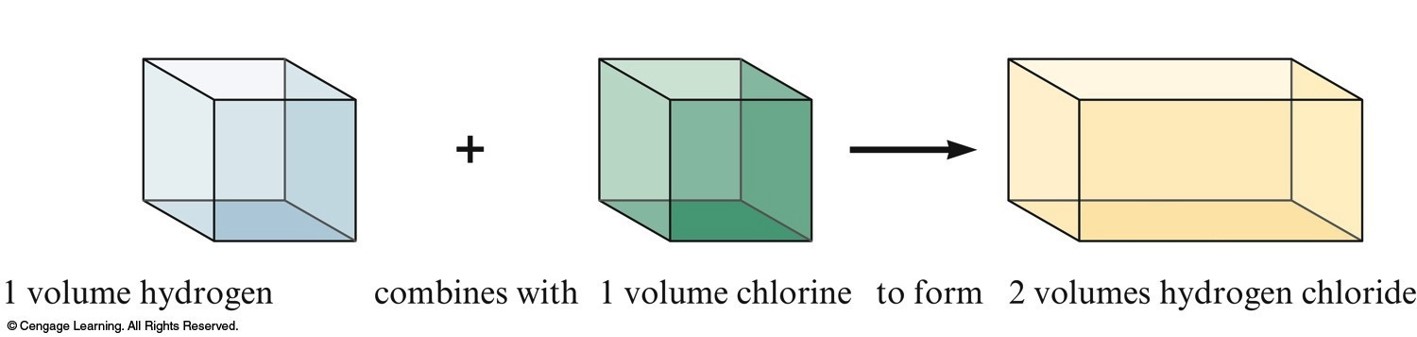
Representing Gay-Lussac's Results 2
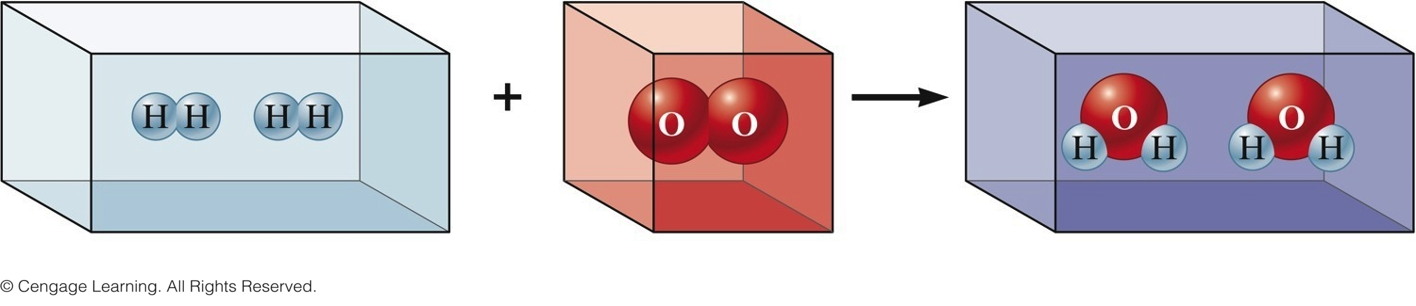
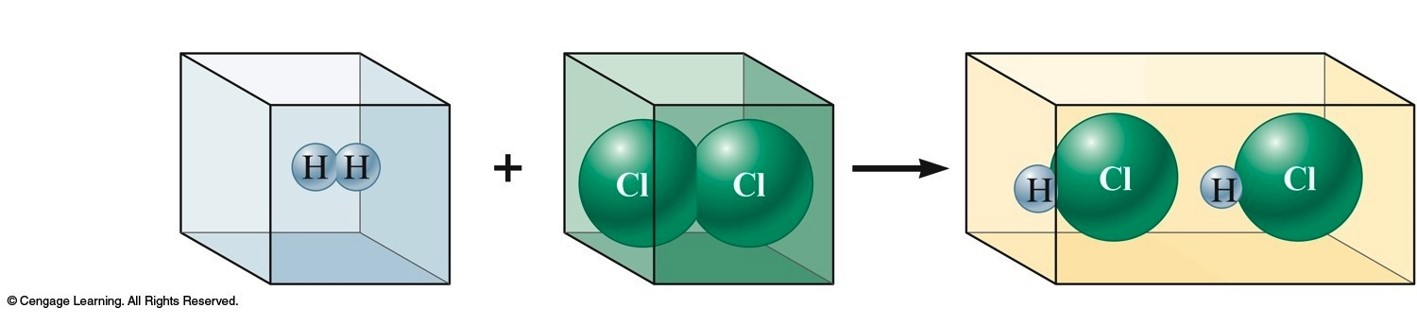
Early Experiments to Characterize the Atom
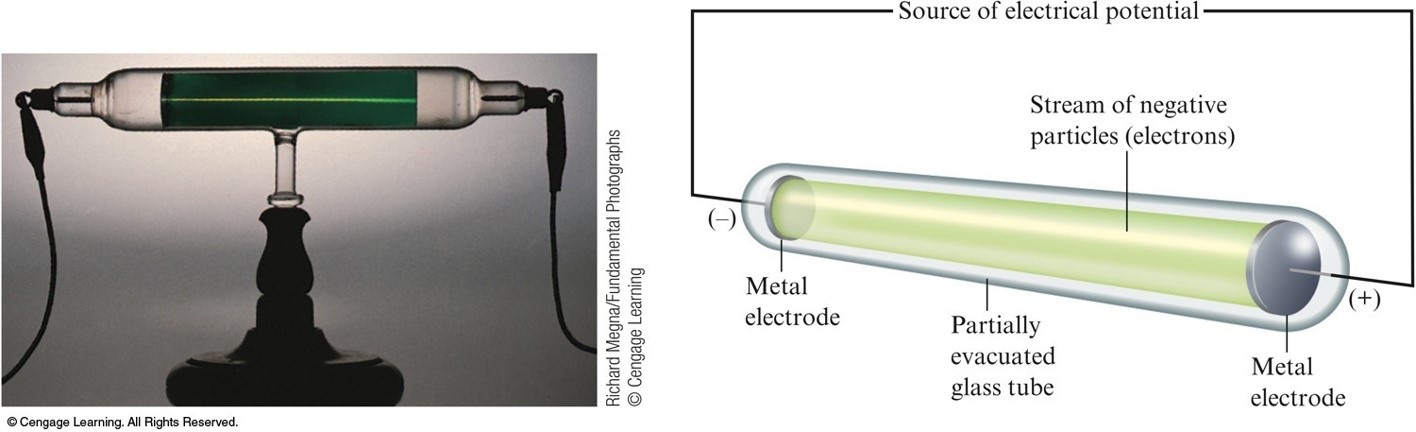
J. J. Thomson (1898-1903)
- Postulated the existence of negatively charged particles, that we now call electrons, using cathode-ray tubes.
- Determined the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron.
- The atom must also contain positive particles that balance exactly the negative charge carried by electrons.
Carthode-Ray Tube
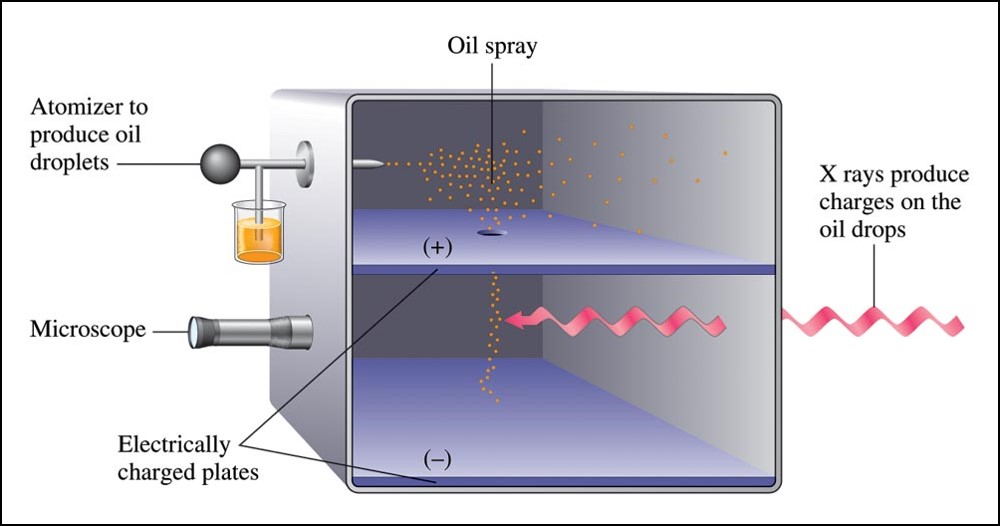
Robert Millikan (1909)
- Performed experiments involving charged oil drops.
- Determined the magnitude of the charge on a single electron.
- Calculated the mass of the electron
- \((9.11 \times 10^{-31}\,\chem{kg})\).
Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
Millikan Oil Drop Experiment - Animation
Henri Becquerel (1896)
- Discovered radioactivity by observing the spontaneous emission of radiation by uranium.
- Three types of radioactive emission exist:
- Gamma rays (\(\gamma\)) – high energy light
- Beta particles (\(\beta\)) – a high speed electron
- Alpha particles (\(\alpha\)) – a particle with a 2+ charge
Ernest Rutherford (1911)
- Explained the nuclear atom.
- The atom has a dense center of positive charge called the nucleus.
- Electrons travel around the nucleus at a large distance relative to the nucleus.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
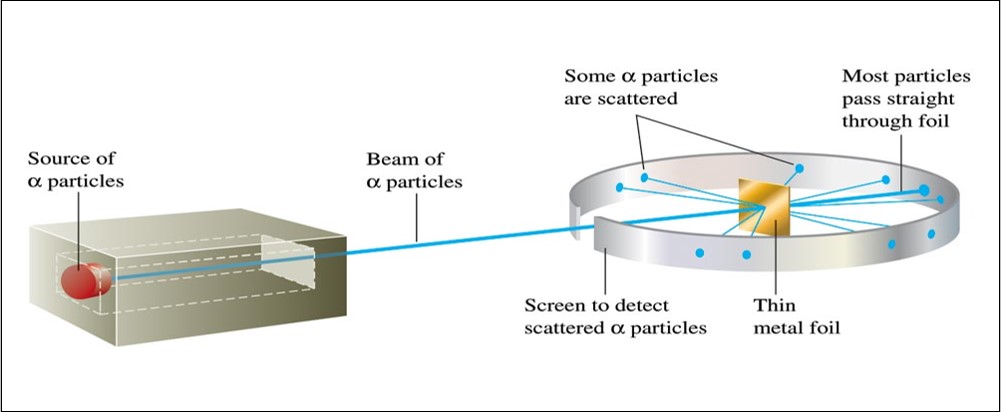
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment - Animation
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment Results
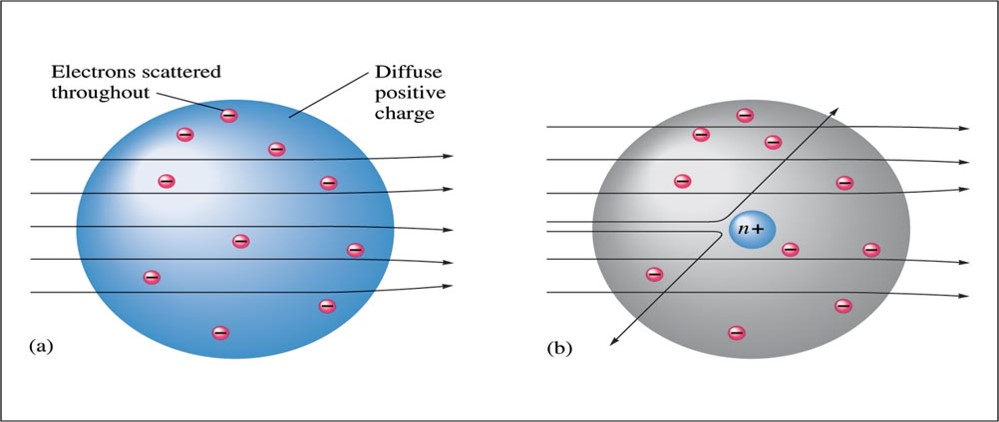
The Modern View of Atomic Structure: An Introduction
The Modern Atom
- The atom contains:
- Electrons – found outside the nucleus; negatively charged.
- Protons – found in the nucleus; positive charge equal in magnitude to the electron’s negative charge.
- Neutrons – found in the nucleus; no charge; virtually same mass as a proton.
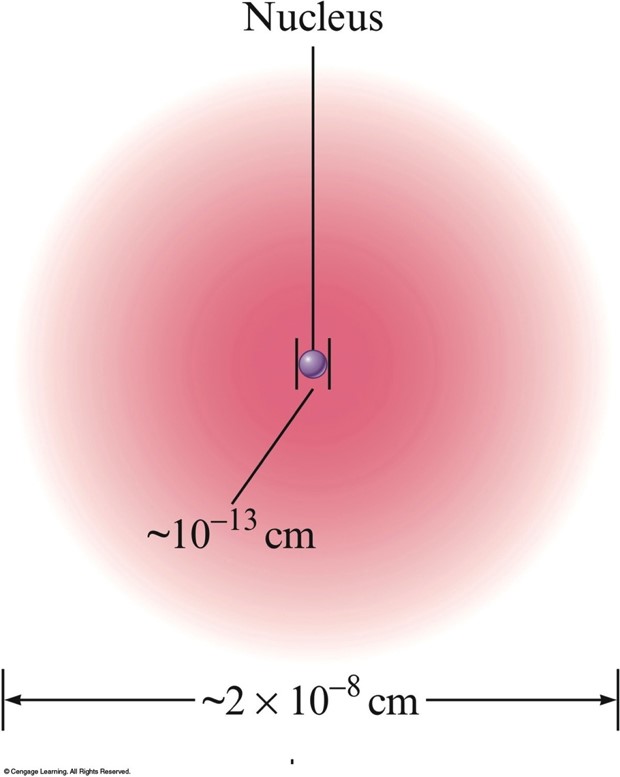
- The nucleus is:
- Small compared with the overall size of the atom.
- Extremely dense; accounts for almost all of the atom’s mass.
Nuclear Atom Viewed in Cross Section
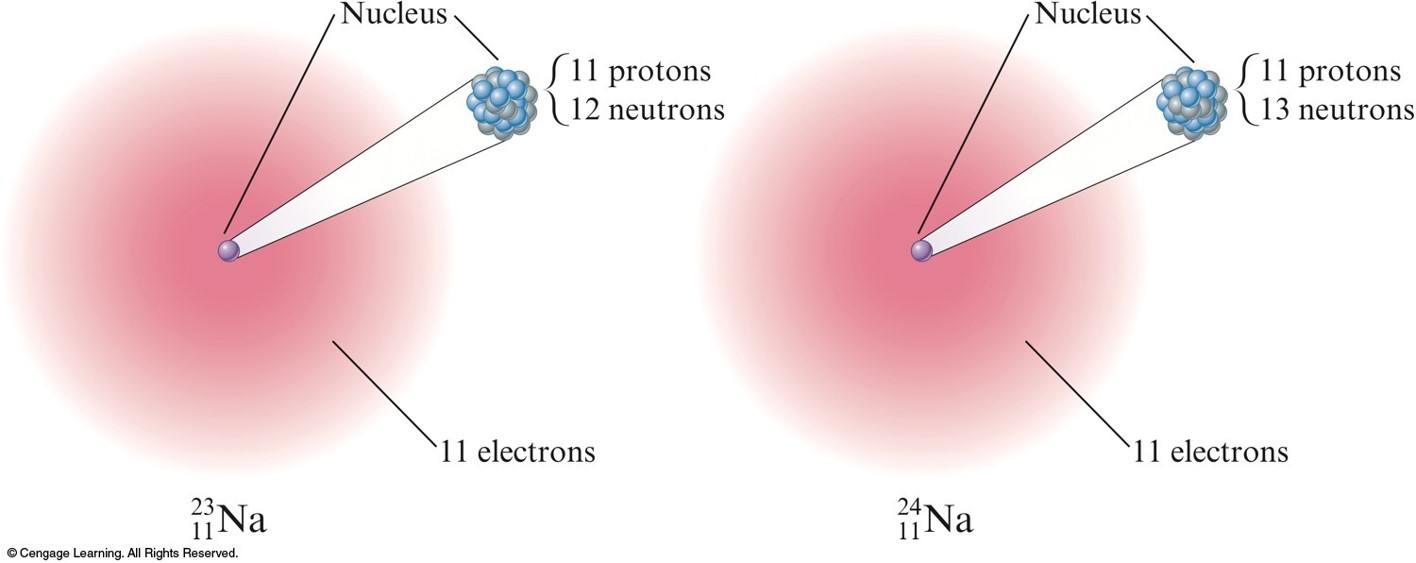
Isotopes
- Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
- Show almost identical chemical properties; chemistry of atom is due to its electrons.
- In nature most elements contain mixtures of isotopes.
Two isotopes of sodium
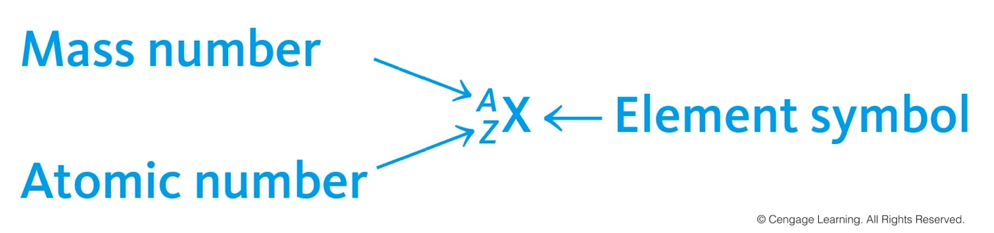
Isotope Symbols
- Isotopes are identified by:
- Atomic Number (Z) – number of protons
- Mass Number (A) – number of protons plus number of neutrons
Molecules and Ions
Chemical Bonds
- Covalent Bonds
- Bonds form between atoms by sharing electrons.
- Resulting collection of atoms is called a molecule.
- Ionic Bonds
- Bonds form due to force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- Ion – atom or group of atoms that has a net positive or negative charge.
- Cation – positive ion; lost electron(s).
- Anion – negative ion; gained electron(s).
An Introduction to the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table
- Metals vs. Nonmetals
- Groups or Families – elements in the same vertical columns; have similar chemical properties
- Periods – horizontal rows of elements
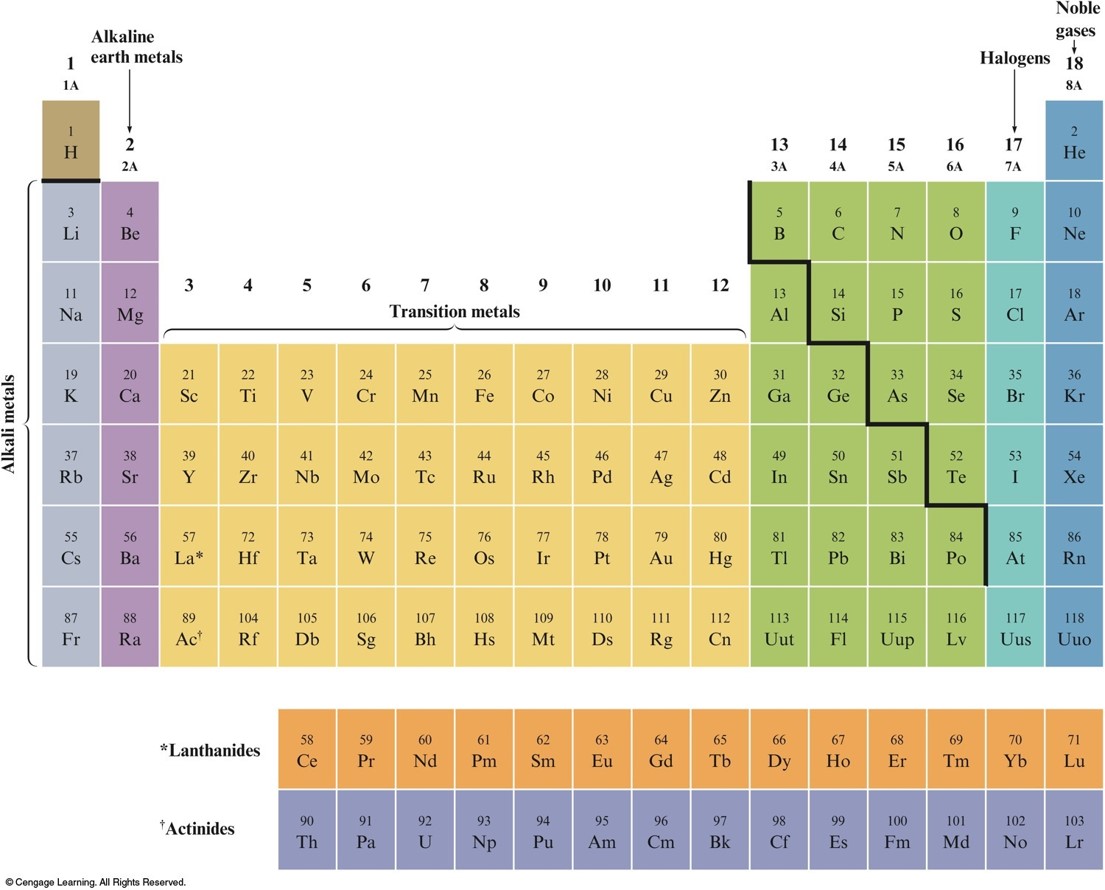
Groups or Families
- Table of common charges formed when creating ionic compounds.
| Group or Family | Charge |
|---|---|
| Alkali Metals (1) | 1+ |
| Alkaline Earth Metals (2) | 2+ |
| Halogens (17) | 1- |
| Noble Gases (18) | 0 |
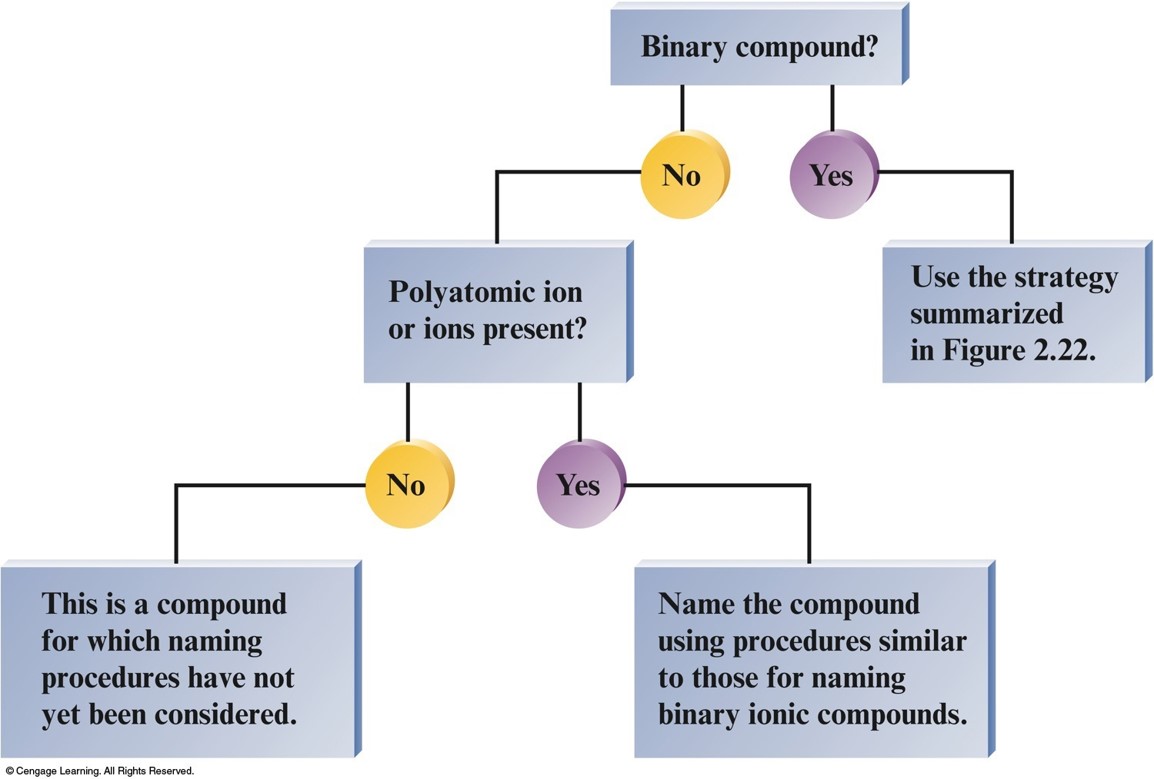
Naming Simple Compounds
Naming Compounds
- Binary Compounds
- Composed of two elements
- Ionic and covalent compounds included
- Binary Ionic Compounds
- Metal—nonmetal
- Binary Covalent Compounds
- Nonmetal—nonmetal
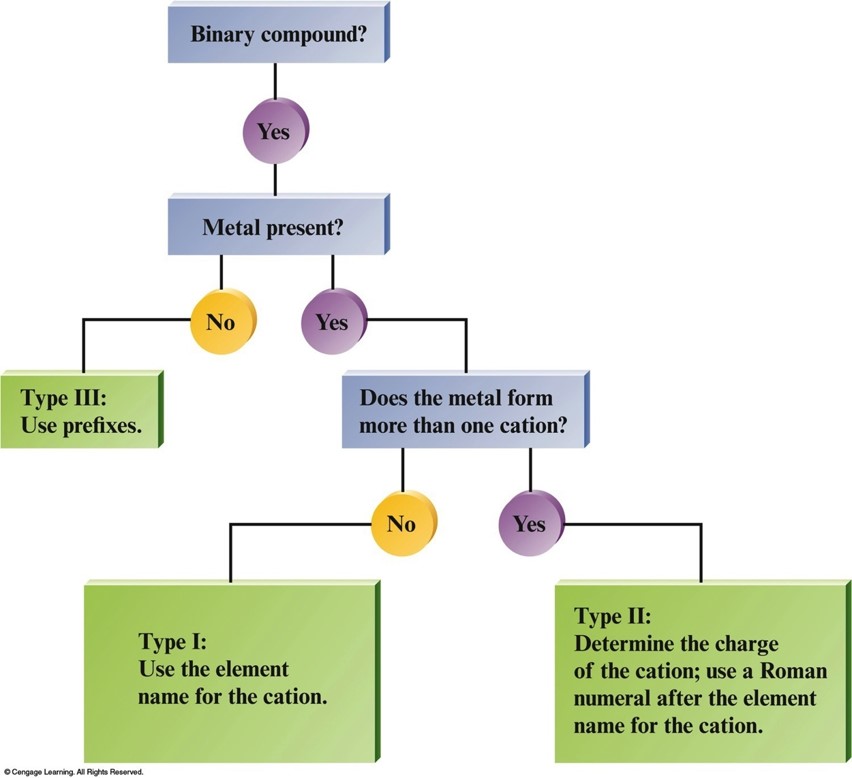
Binary Ionic Compounds (Type I)
- The cation is always named first and the anion second.
- A monatomic cation takes its name from the name of the parent element.
- A monatomic anion is named by taking the root of the element name and adding –ide.
- Examples
- \(\chem{KCl}\) - Potassium chloride
- \(\chem{MgBr_2}\) - Magnesium bromide
- \(\chem{CaO}\) - Calcium oxide
Binary Ionic Compounds (Type II)
- Metals in these compounds form more than one type of positive ion.
- Charge on the metal ion must be specified.
- Roman numeral indicates the charge of the metal cation.
- Transition metal cations usually require a Roman numeral.
- Elements that form only one cation do not need to be identified by a roman numeral.
- Examples
- \(\chem{CuBr}\) - Copper(I) bromide
- \(\chem{FeS}\) - Iron(II) sulfide
- \(\chem{PbO_2}\) - Lead(IV) oxide
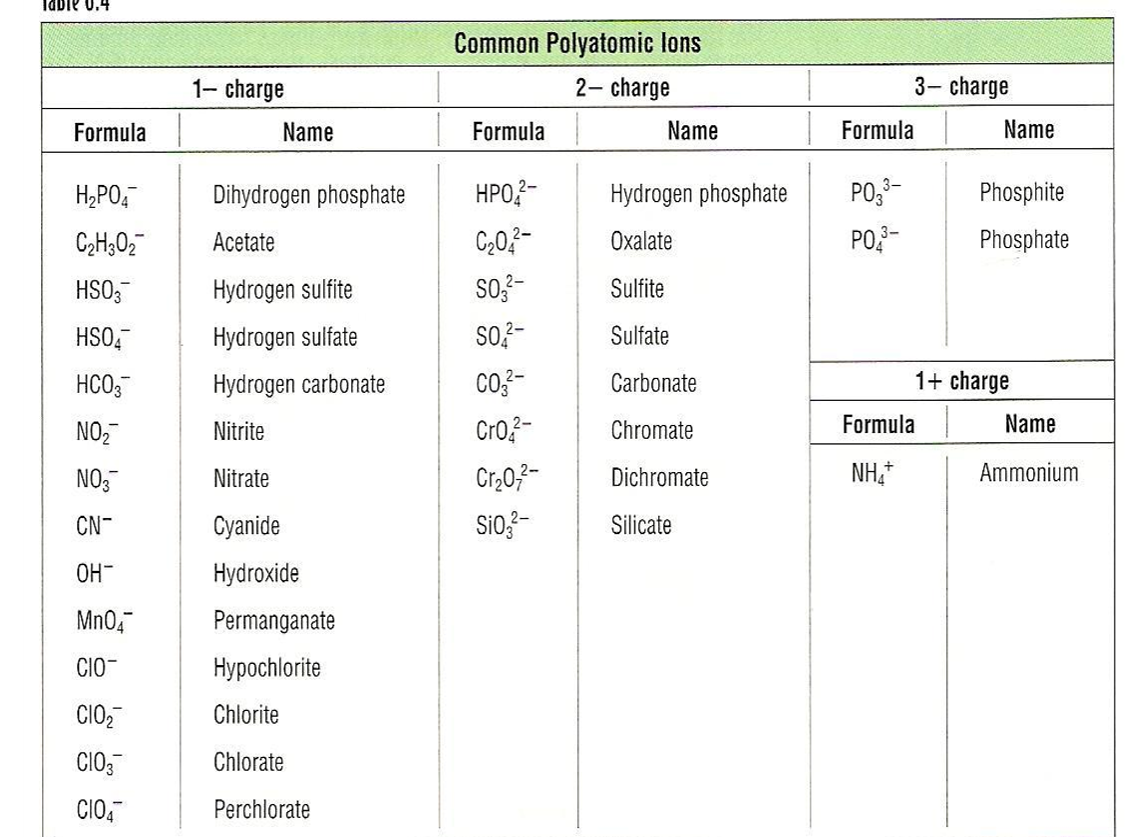
Polyatomic Ions
- Must be memorized (see Table 2.5 on pg. 65 in text).
- Examples of compounds containing polyatomic ions:
- \(\chem{NaOH}\) - Sodium hydroxide
- \(\chem{Mg(NO_3)_2}\) - Magnesium nitrate
- \(\chem{(NH_4)_2SO_4}\) - Ammonium sulfate
Common Polyatomic Ions
Binary Covalent Compounds (Type III)
- Formed between two nonmetals.
- The first element in the formula is named first, using the full element name.
- The second element is named as if it were an anion.
- Prefixes are used to denote the numbers of atoms present.
- The prefix mono- is never used for naming the first element.
| Prefix | Number | Prefix | Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono- | 1 | di- | 2 | |
| tri- | 3 | tetra- | 4 | |
| penta- | 5 | hexa- | 6 | |
| hepta- | 7 | octa- | 8 | |
| nona- | 9 | deca- | 10 |
Binary Covalent Compounds (Type III) - Examples
- \(\chem{CO_2}\) - Carbon dioxide
- \(\chem{SF_6}\) - Sulfur hexafluoride
- \(\chem{N_2O_4}\) - Dinitrogen tetroxide
Flowchart for Naming Binary Compounds
Overall Strategy for Naming Chemical Compounds
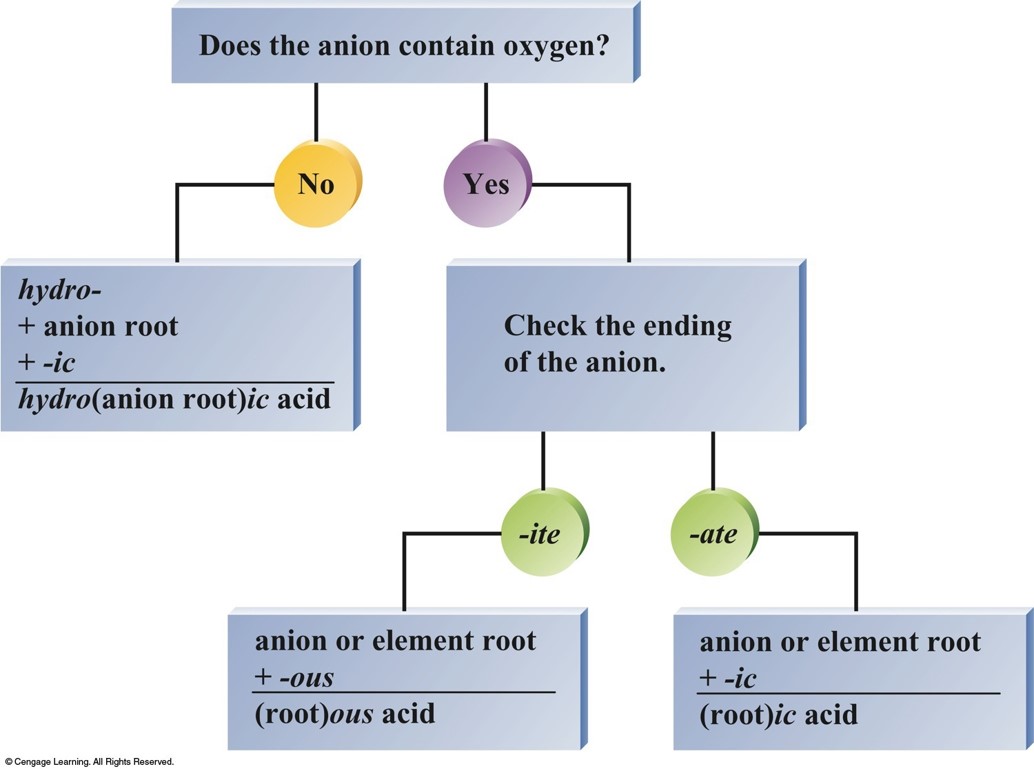
Acids
- Acids can be recognized by the hydrogen that appears first in the formula -\(\chem{HCl}\).
- Molecule with one or more \(\chem{H^+}\) ions attached to an anion.
- If the anion does not contain oxygen, the acid is named with the prefix hydro– and the suffix –ic.
- Examples
- \(\chem{HCl}\) - Hydrochloric acid
- \(\chem{HCN}\) - Hydrocyanic acid
- \(\chem{H_2S}\) - Hydrosulfuric acid
Acids (cont.)
- If the anion does contain oxygen:
- The suffix –ic is added to the root name if the anion name ends in –ate.
- Examples:
- \(\chem{HNO_3}\) - Nitric acid
- \(\chem{H_2SO_4}\) - Sulfuric acid
- \(\chem{HC_2H_3O_2}\) - Acetic acid
- If the anion does contain oxygen:
- The suffix –ous is added to the root name if the anion name ends in –ite.
- Examples:
- \(\chem{HNO_2}\) - Nitrous acid
- \(\chem{H_2SO_3}\) - Sulfurous acid
- \(\chem{HClO_2}\) - Chlorous acid
Flowchart for Naming Acids
/