Chapter 21
Nuclear Chemistry
Shaun Williams, PhD
Review
- Atomic Number (Z) – number of protons
- Mass Number (A) – sum of protons and neutrons $$ {}^A_Z\mathrm{X} $$
Radioactive
- Radioactivity Decay
- Nucleus undergoes decomposition to form a different nucleus.
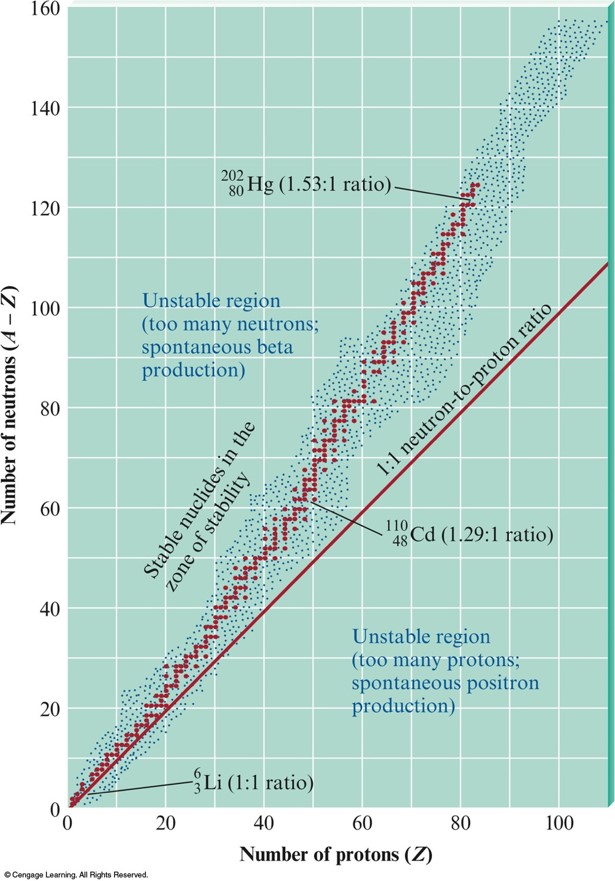
- Radioactive Stability
- Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable.
- Light nuclides are stable when \(Z\) equals \(A – Z\) (neutron/proton ratio is 1).
- For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with \(Z\).
Radioactive Stability
- Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special stability.
- Even numbers of protons and neutrons are more often stable than those with odd numbers.
- Certain specific numbers of protons or neutrons produce especially stable nuclides.
- 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126
The Zone of Stability
Types of Radioactive Decay
- Alpha production (\(\alpha\)) $$ {}^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U} \rightarrow {}^{4}_{2}\chem{He} + {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} $$
- Beta production (\(\beta\)) $$ {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} \rightarrow {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}91}\chem{Pa} + {}^{\phantom{-}0}_{-1}\chem{e} $$
- Gamma ray production (\(\gamma\)) $$ {}^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U} \rightarrow {}^4_2\chem{He} + {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} + 2{}^0_0\gamma $$
- Positron production $$ {}^{22}_{11}\chem{Na} \rightarrow {}^0_1\chem{e} + {}^{22}_{10}\chem{Ne} $$
- Electron capture $$ {}^{201}_{\phantom{0}80}\chem{Hg} + {}^{\phantom{-}0}_{-1}\chem{e} \rightarrow {}^{201}_{\phantom{0}79}\chem{Au} + {}^0_0\gamma $$
Decay Series (Series of Alpha and Beta Decays)
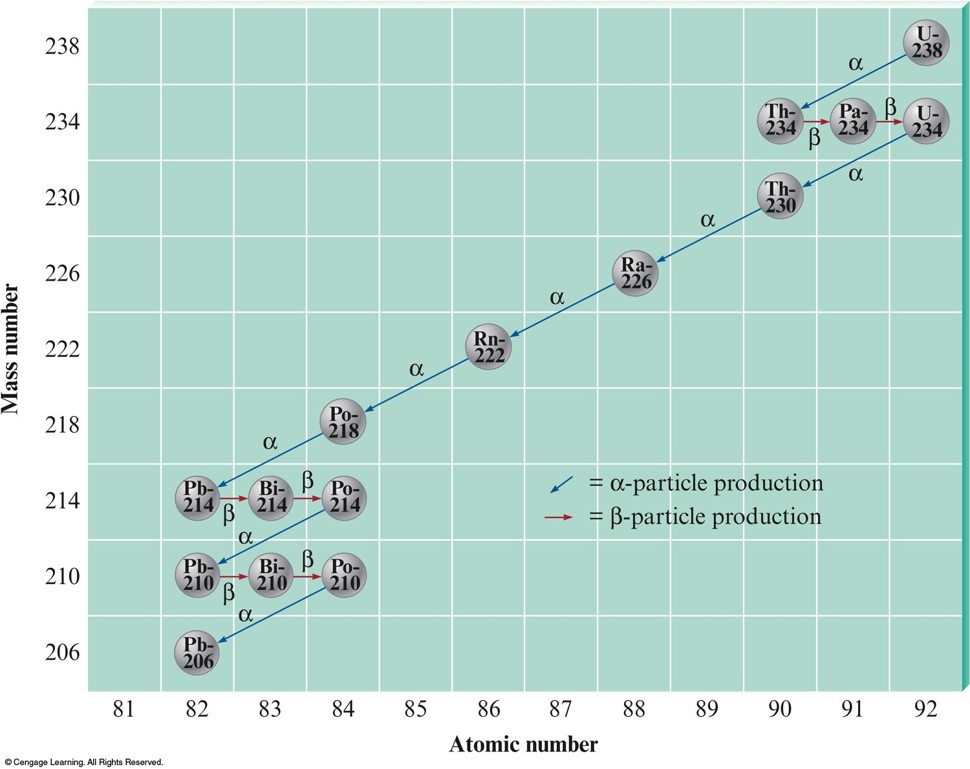
The Half-Lives of Nuclides in the \({}^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U}\) Decay Series
| Decay | Half-Life |
|---|---|
| \( {}^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U} \rightarrow {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} + \alpha \) | \( 4.51 \times 10^9\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} \rightarrow {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}91}\chem{Pa} + \beta \) | \( 24.1\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}91}\chem{Pa} \rightarrow {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U} + \beta \) | \( 6.75\,\mathrm{hours} \) |
| \( {}^{234}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U} \rightarrow {}^{230}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} + \alpha \) | \( 2.48 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{230}_{\phantom{0}90}\chem{Th} \rightarrow {}^{226}_{\phantom{0}88}\chem{Ra} + \alpha \) | \( 8.0 \times 10^4\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{226}_{\phantom{0}88}\chem{Ra} \rightarrow {}^{222}_{\phantom{0}86}\chem{Rn} + \alpha \) | \( 1.62 \times 10^3\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{222}_{\phantom{0}86}\chem{U} \rightarrow {}^{218}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} + \alpha \) | \( 3.82\,\mathrm{days} \) |
| \( {}^{218}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} \rightarrow {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}82}\chem{Pb} + \alpha \) | \( 3.1\,\mathrm{minutes} \) |
The Half-Lives of Nuclides in the \({}^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\chem{U}\) Decay Series Continued
| Decay | Half-Life |
|---|---|
| \( {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}82}\chem{Pb} \rightarrow {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}83}\chem{Bi} + \beta \) | \( 26.8\,\mathrm{minutes} \) |
| \( {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}83}\chem{Bi} \rightarrow {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} + \beta \) | \( 19.7\,\mathrm{minutes} \) |
| \( {}^{214}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} \rightarrow {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}82}\chem{Pb} + \alpha \) | \( 1.6 \times 10^{-4}\,\mathrm{seconds} \) |
| \( {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}82}\chem{Pb} \rightarrow {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}83}\chem{Bi} + \beta \) | \( 20.4\,\mathrm{years} \) |
| \( {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}83}\chem{Bi} \rightarrow {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} + \beta \) | \( 5.0\,\mathrm{days} \) |
| \( {}^{210}_{\phantom{0}84}\chem{Po} \rightarrow {}^{206}_{\phantom{0}82}\chem{Pb} + \alpha \) | \( 138.4\,\mathrm{days} \) |
Radioactive Decay Kinetics
- Decay rate $$ \mathrm{Rate}=kN $$
- The rate of decay is proportional to the number of nuclides.
- Half-Life - Time required for the number of nuclides to reach half the original value. $$ t_\bfrac{1}{2} = \frac{\ln(2)}{k} = \frac{0.693}{k} $$
Exercise
A first order reaction is 35% complete at the end of 55 minutes. What is the value of \(k\)?
\( k = 7.8 \times 10^{-3}\,\mathrm{min}^{-1} \)
Nuclear Transformation
- The change of one element into another. $$ \begin{align} {}^{27}_{13}\chem{Al} + {}^4_2\chem{He} &\rightarrow {}^{30}_{15}\chem{P} + {}^1_0\chem{n} \\ {}^{249}_{\phantom{0}98}\chem{Cf} + {}^{18}_{\phantom{0}8}\chem{O} &\rightarrow {}^{263}_{106}\chem{Sg} + 4{}^1_0\chem{n} \end{align} $$
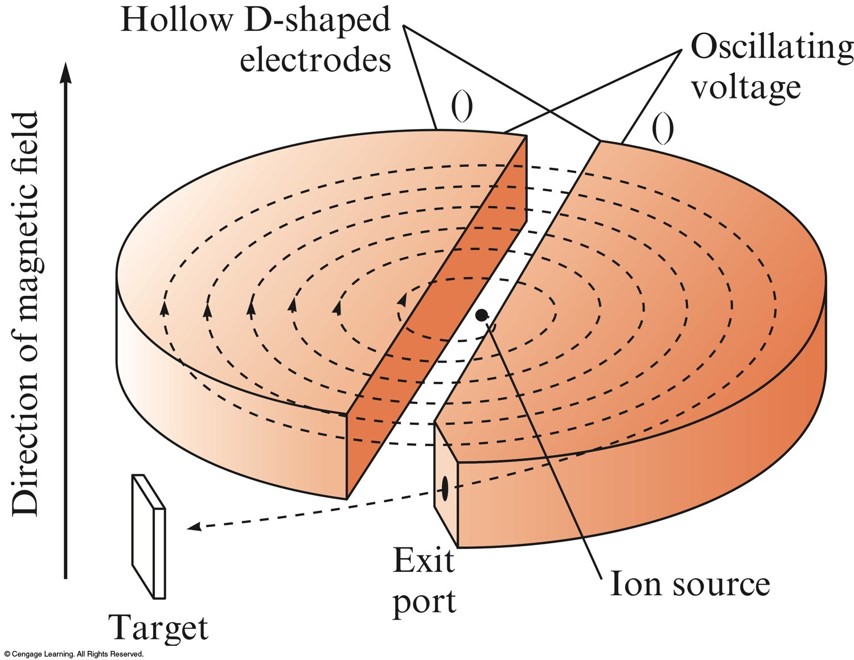
A Schematic Diagram of a Cyclotron

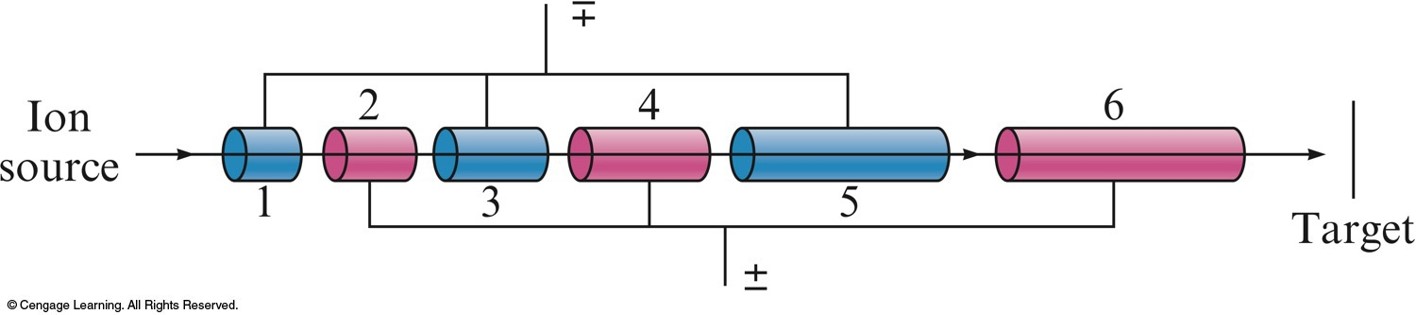
A Schematic Diagram of a Linear Accelerator
Measuring Radioactivity Levels
- Geiger counter
- Scintillation counter
Geiger-Muller Counter
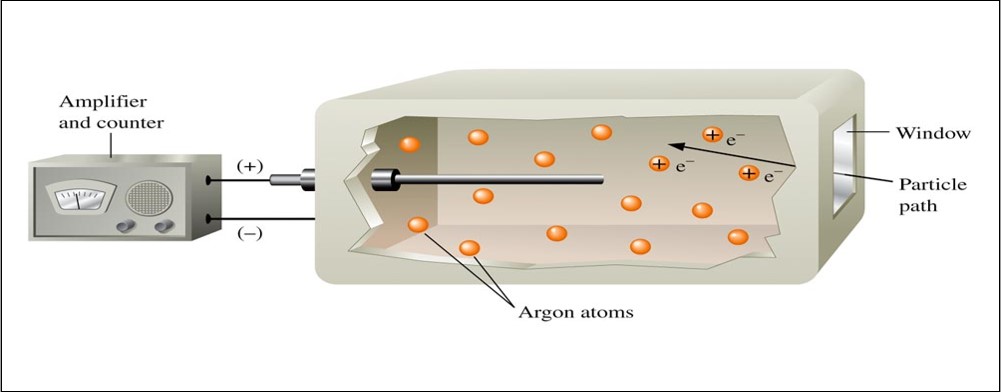
Carbon-14 Dating
- Used to date wood and cloth artifacts.
- Based on carbon–14 to carbon–12 ratio.
Radiotracers
- Radioactive nuclides that are introduced into organisms in food or drugs and whose pathways can be traced by monitoring their radioactivity.
| Nuclide | Half-Life | Area of the Body Studied |
|---|---|---|
| \( {}^{131}\chem{I} \) | 8.0 days | Thyroid |
| \( {}^{59}\chem{Fe} \) | 44.5 days | Red blood cells |
| \( {}^{99}\chem{Mo} \) | 66 hours | Metabolism |
| \( {}^{32}\chem{P} \) | 14.3 days | Eyes, liver, tumors |
| \( {}^{51}\chem{Cr} \) | 27.7 days | Red blood cells |
| \( {}^{87}\chem{Sr} \) | 2.8 hours | Bones |
| \( {}^{99m}\chem{Tc} \) | 6.0 hours | Heart, bones, liver, and lungs |
| \( {}^{133}\chem{Xe} \) | 5.2 days | Lungs |
| \( {}^{24}\chem{Na} \) | 15.0 hours | Circulatory system |
Energy and Mass
- When a system gains or loses energy it also gains or loses a quantity of mass. $$ \begin{align} \Delta E &= \Delta mc^2 \\ \Delta m &= \text{mass defect} \\ \Delta E &= \text{change in energy} \end{align} $$
- If \(\Delta E\) is negative (exothermic), mass is lost from the system.
Mass Defect (\( \Delta m\))
- Calculating the mass defect for \( {}^4_2\chem{He} \):
- Since atomic masses include the masses of the electrons, we must account for the electron mass.
- \( {}^4_2\chem{He} \) nucleus is “synthesized” from 2 protons and two neutrons. $$ \begin{align} \Delta m &= \left( 4.0026 - 2m_e \right) - \left[ 2\left( 1.0078-m_e \right) +2\left( 1.0087 \right) \right] \\ \Delta m &= -0.0304\,\mathrm{amu} \end{align} $$
Binding Energy
- The energy required to decompose the nucleus into its components.
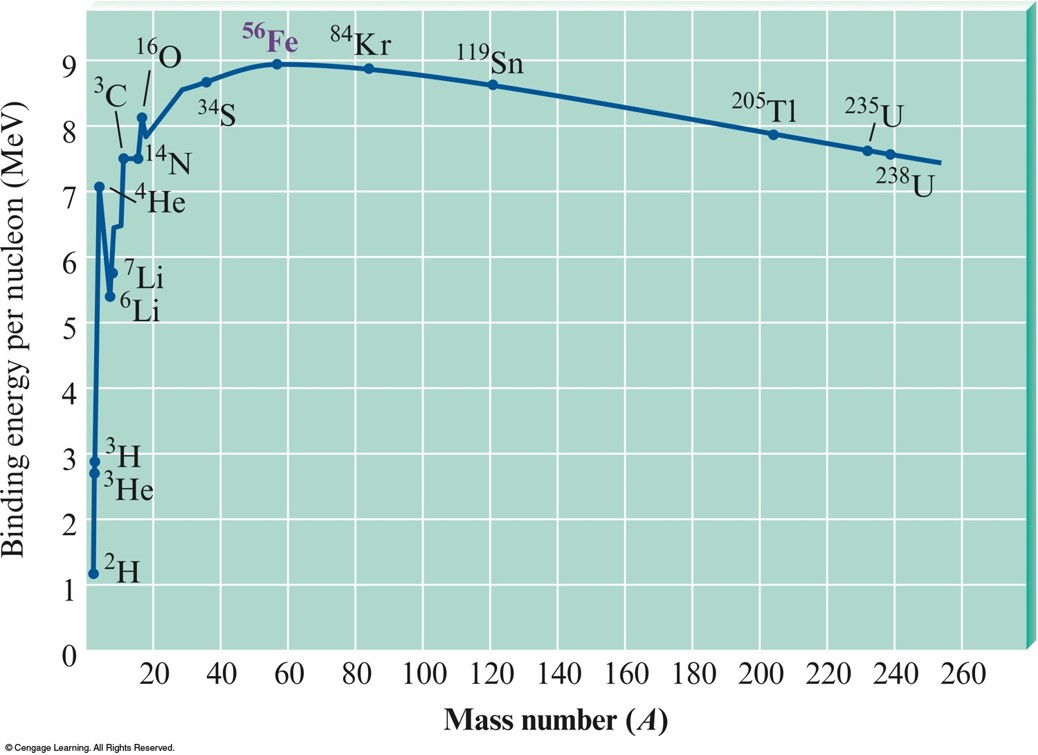
- Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus and has a binding energy of 8.79 MeV.
Binding Energy per Nucleon vs. Mass Number
Nuclear Fission and Fusion
- Fusion – Combining two light nuclei to form a heavier, more stable nucleus. $$ \chem{{}^3_2He + {}^1_1H \rightarrow {}^4_2He + {}^0_1e} $$
- Fission – Splitting a heavy nucleus into two nuclei with smaller mass numbers. $$ \chem{{}^1_0n + {}^{235}_{\phantom{0}92}U \rightarrow {}^{142}_{\phantom{0}56}Ba + {}^{91}_{36}Kr + 3{}^1_0n} $$
Fission Processes
- A self-sustaining fission process is called a chain reaction.
| Event | Neutron Causing Fission Event |
Result |
|---|---|---|
| subscritical | \(<1\) | reaction stops |
| critical | \(=1\) | sustained reaction |
| supercritical | \(>1\) | violet explosion |
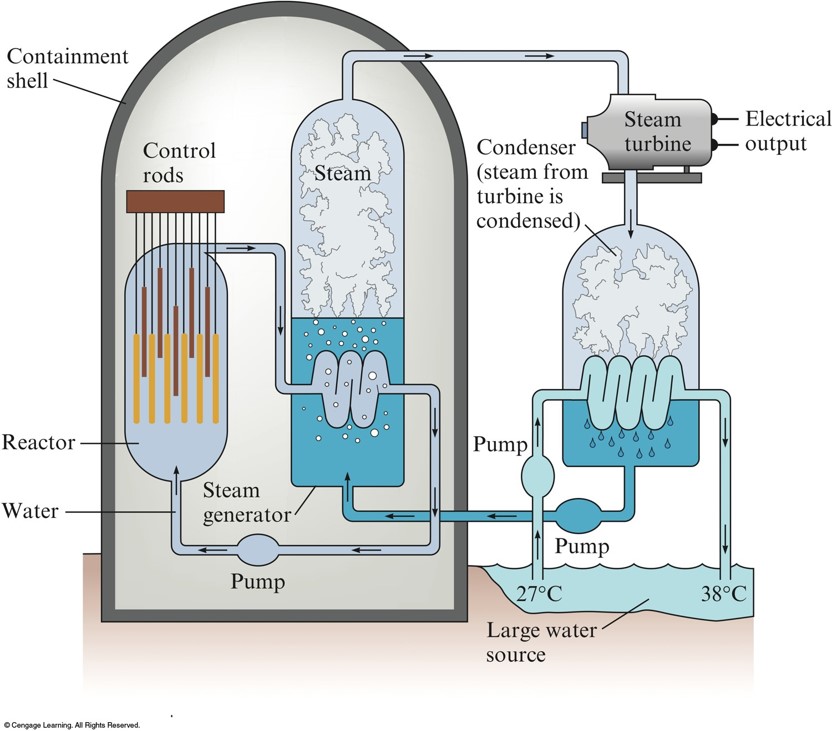
Schematic Diagram of a Nuclear Power Plant
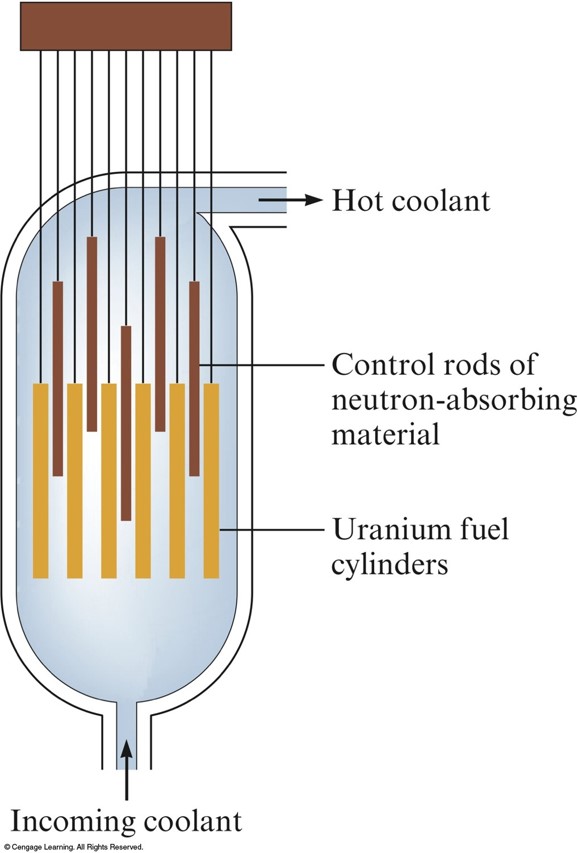
Schematic Diagram of a Reactor Core
Biological Effects of Radiation
Depends on:
- Energy of the radiation
- Penetrating ability of the radiation
- Ionizing ability of the radiation
- Chemical properties of the radiation source
rem (roentgen equivalent for man)
- The energy dose of the radiation and its effectiveness in causing biologic damage must be taken into account. $$ \begin{align} \text{Number of rems} =& \left( \text{number of rads} \right) \times \mathrm{RBE} \\ \mathrm{rads} =& \text{radiation absorbed dose} \\ \mathrm{RBE} =& \text{relative effectiveness of the} \\ & \text{radiation in causing biologic damage} \end{align} $$
Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Radiation
| Dose (rem) | Clinical Effect |
|---|---|
| 0-25 | Nondetectable |
| 25-50 | Temporary decrease in white blood cell counts |
| 100-200 | Strong decrease in white blood cell counts |
| 500 | Death of half the exposed population within 30 days after exposure |
/