Chapter 1
Essential Ideas
Shaun Williams, PhD
Chemistry: An Overview
Why chemistry seems hard
- A main challenge of chemistry is to understand the connection between the macroscopic world that we experience and the microscopic world of atoms and molecules.
- You must learn to think on the atomic level.
Atoms vs. Molecules
- Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms.
- Atom: smallest part of an element that is still that element.
- Molecule: Two or more atoms joined and acting as a unit.
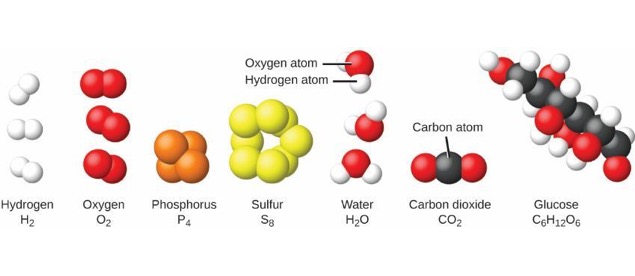
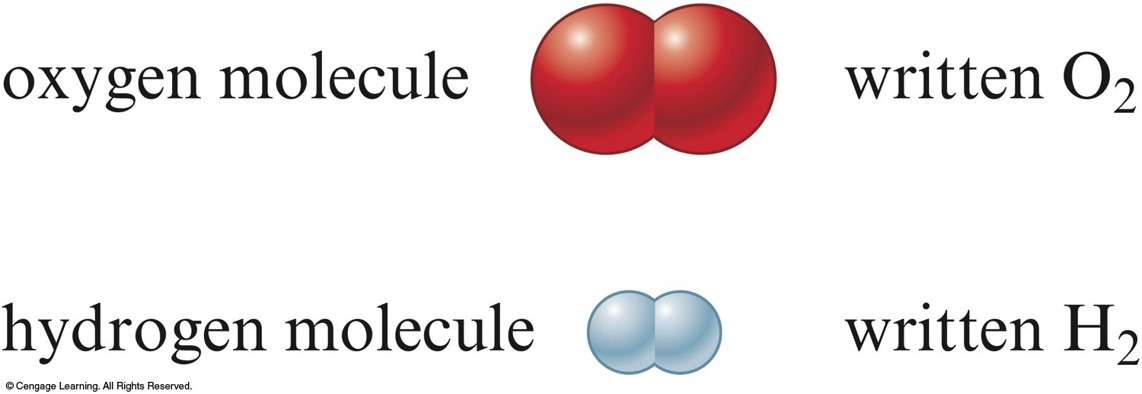
Oxygen and Hydrogen Molecules
- Use subscripts when more than one atom is in the molecule.
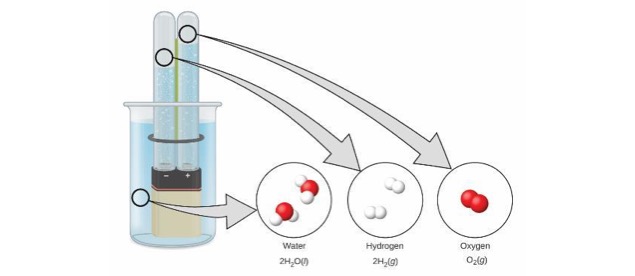
A Chemical Reaction
- One substance changes to another by reorganizing the way the atoms are attached to each other.
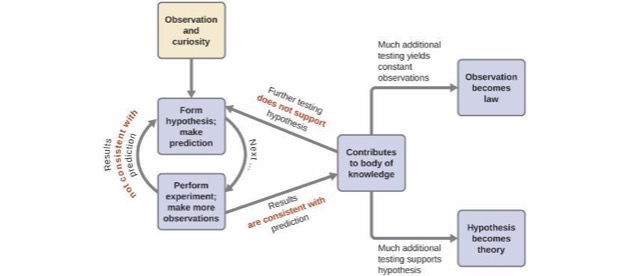
The Scientific Method
Science
- Science is a framework for gaining and organizing knowledge.
- Science is a plan of action — a procedure for processing and understanding certain types of information.
- Scientists are always challenging our current beliefs about science, asking questions, and experimenting to gain new knowledge.
- Scientific method is needed.
Fundamental Steps of the Scientific Method
- Process that lies at the center of scientific inquiry.
Scientific Models
- Law - A summary of repeatable observed (measurable) behavior.
- Hypothesis - A possible explanation for an observation.
- Theory (Model) - Set of tested hypotheses that gives an overall explanation of some natural phenomenon.
Units of Measurement
Nature of Measurement
Measurement
- Quantitative observation consisting of two parts.
- number
- scale (unit)
- Examples
- \(20\, \chem{grams}\)
- \( 6.63 \times 10^{-34}\,\chem{J}\cdot\chem{second}\)
The Fundamental SI Units
| Physical Quantity | Name of Unit | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Length | meter | m |
| Time | second | s |
| Temperature | kelvin | K |
| Electric current | ampere | A |
| Amount of substance | mole | mol |
| Luminous intensity | candela | cd |
Prefixes Used in the SI System
- Prefixes are used to change the size of the unit.
| Prefix | Symbol | Meaning | Exponential Notation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exa | \(\chem{E}\) | \(1,000,000,000,000,000,000\) | \(10^{18}\) |
| peta | \(\chem{P}\) | \(1,000,000,000,000,000\) | \(10^{15}\) |
| tera | \(\chem{T}\) | \(1,000,000,000,000\) | \(10^{12}\) |
| giga | \(\chem{G}\) | \(1,000,000,000\) | \(10^{9}\) |
| mega | \(\chem{M}\) | \(1,000,000\) | \(10^{6}\) |
| kilo | \(\chem{k}\) | \(1,000\) | \(10^3\) |
| hecto | \(\chem{h}\) | \(100\) | \(10^2\) |
| deka | \(\chem{da}\) | \(10\) | \(10^1\) |
| - | \(-\) | \(1\) | \(10^0\) |
More Prefixes Used in the SI System
| Prefix | Symbol | Meaning | Exponential Notation |
|---|---|---|---|
| deci | \(\chem{d}\) | \(0.1\) | \(10^{-1}\) |
| centi | \(\chem{c}\) | \(0.01\) | \(10^{-2}\) |
| milli | \(\chem{m}\) | \(0.001\) | \(10^{-3}\) |
| micro | \(\chem{\mu}\) | \(0.000001\) | \(10^{-6}\) |
| nano | \(\chem{n}\) | \(0.000000001\) | \(10^{-9}\) |
| pico | \(\chem{p}\) | \(0.000000000001\) | \(10^{-12}\) |
| femto | \(\chem{f}\) | \(0.00000000000001\) | \(10^{-15}\) |
| atto | \(\chem{a}\) | \(0.000000000000000001\) | \(10^{-18}\) |
Mass \(\ne\) Weight
- Mass is a measure of the resistance of an object to a change in its state of motion. Mass does not vary.
- Weight is the force that gravity exerts on an object. Weight varies with the strength of the gravitational field.
Uncertainty in Measurement
Uncertainty in measurements
- A digit that must be estimated in a measurement is called uncertain.
- A measurement always has some degree of uncertainty. It is dependent on the precision of the measuring device.
- Record the certain digits and the first uncertain digit (the estimated number).
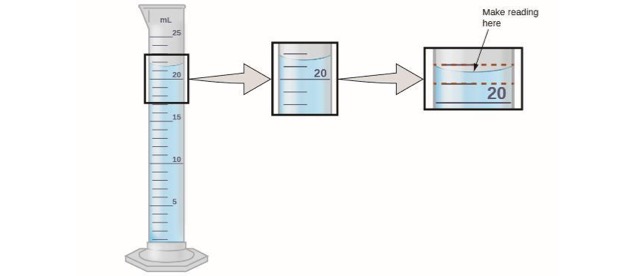
Measurement of Volume Using a Buret
- The volume is read at the bottom of the liquid curve (meniscus).
- Meniscus of the liquid occurs at about 20.15 mL.
- Certain digits: 20.15
- Uncertain digit: 20.15
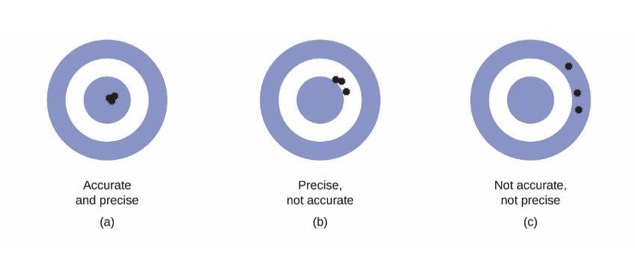
Precision and Accuracy
- Accuracy - Agreement of a particular value with the true value.
- Precision - Degree of agreement among several measurements of the same quantity.
Precision and Accuracy: Graphically
Significant Figures and Calculations
Rules for Counting Significant Figures
- Underline the left-most, nonzero digit.
- \(\underline{2}73.1023\)
- \(0.\underline{1}023\)
- \(0.\underline{7}10\)
- \(\underline{1}0.025\)
- \(\underline{1}020\)
Rules for Counting Significant Figures (cont.)
- We look to a decimal point.
- If the number contains a decimal point, underline the right-most digit.
- \(\underline{2}73.102\underline{3}\)
- \(0.\underline{1}02\underline{3}\)
- \(0.\underline{7}1\underline{0}\)
- \(\underline{1}0.02\underline{5}\)
- If the number does not contain a decimal point, underline the right-most, nonzero digit.
- \(\underline{1}0\underline{2}0\)
- If the number contains a decimal point, underline the right-most digit.
Rules for Counting Significant Figures (concluded)
- Count the numbers from one underlined number to the other.
- \(\underline{2}73.102\underline{3}\) has 7 sig. figs.
- \(0.\underline{1}02\underline{3}\) has 4 sig. figs.
- \(0.\underline{7}1\underline{0}\) has 3 sig. figs.
- \(\underline{1}0.02\underline{5}\) has 5 sig. figs.
- \(\underline{1}0\underline{2}0\) has 3 sig. figs.
Special Types of Numbers
- Exact numbers have an infinite number of significant figures.
- \(1\,\chem{inch}=2.54\,\chem{cm}\), exactly (by definition).
- \(9\) pencils (obtained by counting).
Exponential Notation
- Example
- \(300.\) written as \(3.00 \times 10^2\)
- Contains three significant figures.
- Two Advantages
- Number of significant figures can be easily indicated.
- Fewer zeros are needed to write a very large or very small number.
Significant Figures in Mathematical Operations
- For multiplication or division, the number of significant figures in the result is the same as the number in the least precise measurement used in the calculation. $$ 1.342 \times \underline{5.5} = 7.381 \xrightarrow{\chem{round}} \underline{7.4} $$
- For addition or subtraction, the result has the same number of decimal places as the least precise measurement used in the calculation. $$ 23.445 + 7.8\underline{3} = 31.275 \xrightarrow{\chem{round}} 31.2\underline{8} $$
Dimensional Analysis
Converting between unit systems
- Use when converting a given result from one system of units to another.
- To convert from one unit to another, use the equivalence statement that relates the two units.
- Derive the appropriate unit factor by looking at the direction of the required change (to cancel the unwanted units).
- Multiply the quantity to be converted by the unit factor to give the quantity with the desired units.
Example #1
A golfer putted a golf ball 6.8 ft across a green. How many inches does this represent?
- To convert from one unit to another, use the equivalence statement that relates the two units. $$ 1\,\chem{ft} = 12\,\chem{in} $$ The two unit factors are: $$ \frac{1\,\chem{ft}}{12\,\chem{in}}\;\chem{and}\; \frac{12\,\chem{in}}{1\,\chem{ft}} $$
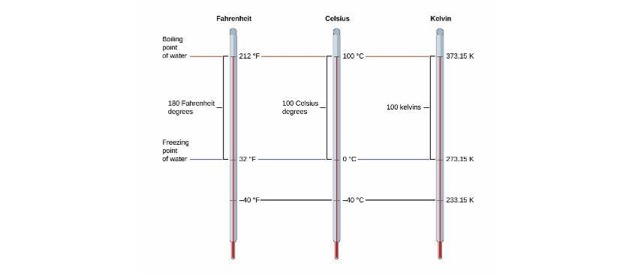
Temperature
Three Systems for Measuring Temperature
- Fahrenheit
- Celsius
- Kelvin
Density
- Mass of substance per unit volume of the substance.
- Common units are \(\bfrac{\chem{g}}{\chem{cm^3}}\) or \(\bfrac{\chem{g}}{\chem{mL}}\).
Density Example 1
Calculate the density of a \( 0.03020\,L\) sample of ethanol with a mass of \( 23.71002\,g\).
Density Example 2
What is the volume of an object that has a density of \( 10.2\bfrac{g}{mL}\) and a mass of \( 30.0\,kg\)?
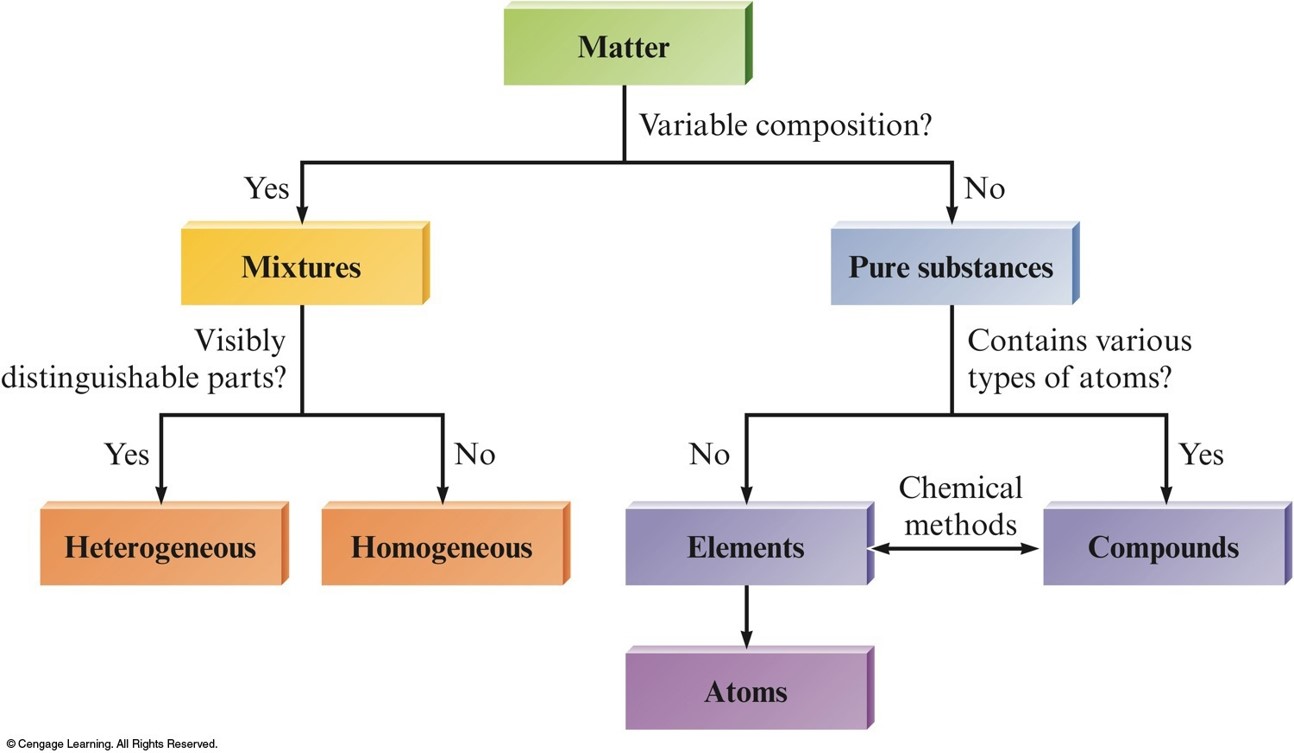
Classification of Matter
Matter
- Anything occupying space and having mass.
- Matter exists in three states.
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
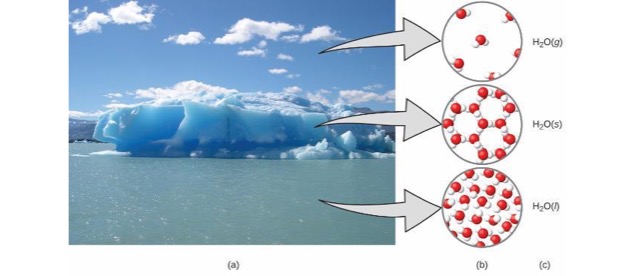
The Phases - Macroscopically
- Solid
- Rigid
- Has fixed volume and shape.
- Liquid
- Has definite volume but no specific shape.
- Assumes shape of container.
- Gas
- Has no fixed volume or shape.
- Takes on the shape and volume of its container.
Mixtures
Have variable composition.
- Homogeneous mixture - Having visibly indistinguishable parts; solution.
- Heterogeneous mixture - Having visibly distinguishable parts.
Pure Substances
Have a single composition.
- Element - A pure substance that cannot be broken down using chemical reactions.
- Compound - A pure substance that can be broken down using chemical reactions.
Physical Change
- Change in the form of a substance, not in its chemical composition.
- Example: boiling or freezing water
- Can be used to separate a mixture into pure compounds, but it will not break compounds into elements.
- Distillation
- Filtration
- Chromatography
Chemical Change
- A given substance becomes a new substance or substances with different properties and different composition.
- Example: Bunsen burner (methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water)
Concept Check!
Which of the following are examples of a chemical change?
- Pulverizing (crushing) rock salt
- Burning of wood
- Dissolving of sugar in water
- Melting a popsicle on a warm summer day
Concept Check! Answer
Which of the following are examples of a chemical change?
- Pulverizing (crushing) rock salt
- Burning of wood
- Dissolving of sugar in water
- Melting a popsicle on a warm summer day
The Organization of Matter
/